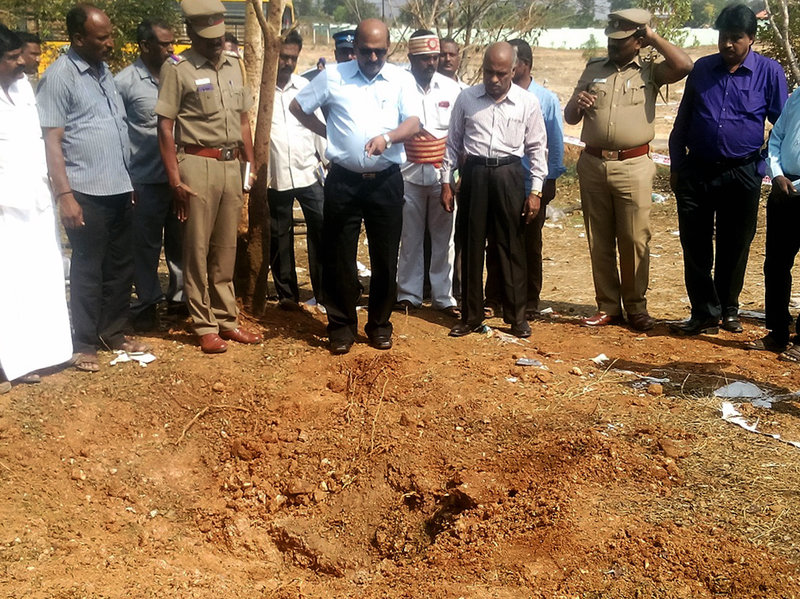
A man was killed and three others were injured last week in the southern Indian state of Tamil Nadu after a meteorite fell in the Vellore campus of a private engineering college. While the man, a 40-year-old bus driver, was reportedly thrown 10 feet into the air by the impact, the explosion created a two feet deep crater and shattered the windows of classrooms and the windshields of vehicles parked in the vicinity.
Indian authorities believe a meteorite may have killed a man — the first such death in recorded history >> https://t.co/492vYrguzG
— Discovery (@Discovery) February 9, 2016
Although the state government described the incident as a meteorite strike and promised 100,000 INR ($1471) to the family of the deceased and 25,000 INR ($368) to each of the three injured victims. Although it would have been the first time in modern history that a human being had been killed by a meteorite; NASA said in a statement that the man was not likely killed by anything extraterrestrial.
“Initial assessments, based on photos posted online, are not consistent with something from space. Small meteorites do not start fires or cause explosions when they hit the ground. To form a crater the size of what has been posted online would have required a meteorite of at least several kilograms. While more details are forthcoming from local scientists, this is unlikely something from space.”
According to NASA, an individual’s chance of being killed by a meteorite is small, but the risk increases with the size of the impacting comet or asteroid, with the greatest risk associated with global catastrophes resulting from impacts of objects larger than 1 kilometer.
A meteorite is a meteoroid – a small particle from an asteroid or comet that goes around the sun – that survives entry into the atmosphere and falls to Earth.
Sujan Sengupta, an associate professor at the Indian Institute of Astrophysics, also believed there was extremely little possibility of a small meteorite falling to the ground and killing someone.
“If a bigger asteroid enters the Earth’s atmosphere, it will disintegrate and travel in different directions and because most of the Earth’s surface is covered in water, it is most likely to fall into the ocean.”
Lindley Johnson, NASA’s planetary defense officer, told The New York Times:
“A death by meteorite impact is so rare that one has never been scientifically confirmed in recorded history. There have been reports of injuries, but even those were extremely rare before the Chelyabinsk event three years ago [referring to a 2013 episode in Russia that left more than 1,000 people injured].”
So what could have fallen from the sky?
Scientists like Dr. Spears, a meteorite and asteroid expert at NASA’s Space Science Division, believe the most likely cause could be an object falling from an aircraft. Another, less likely cause, could be space junk.
Meteorite Kills Man: Police First Suspected Bombing Killed Indian Bus Driver https://t.co/BcEP3hQfqx pic.twitter.com/1aijXwMWJC
— Lead Stories (@LeadStoriesCom) February 8, 2016
Indian scientists are investigating the man’s death and claims that he was killed by an explosion caused by a meteorite. Scientists from the Indian Institute of Astrophysics are analyzing samples of the rock that fell from the sky to determine if it was a meteorite, falling space junk or some other form of debris.
“The probability of being killed by a meteorite is negligible, even witnessing one fall is rare. A fact-finding team of scientists is in Vellore to examine the crater and residue,” said Dr Harsh Vardhan, India’s minister for Science and Technology.
Could it be a piece from NoKo’s rocket/satellite? Meteorite Like Object Kills Man in Vellore https://t.co/DJjWCoU3gZ via @NewIndianXpress
— Ripu_Mardanan (@lsk2007) February 8, 2016
Considering there was neither any prediction of a meteorite shower, nor any meteorite shower was observed, this certainly is a rare phenomenon if it is a meteorite…
This Article (“First Recorded Fatality From A Meteorite” Leaves NASA, Experts Perplexed) is a free and open source. You have permission to republish this article under a Creative Commons license with attribution to the author and AnonHQ.com.