Written by: Brandon C.
There aren’t many doctors in underdeveloped countries, so what do the people do when they need a doctor? Most try to fight it or go to traditional healers, but some new technology has been created that could save lots of lives. A new device that can transmit electrochemical analysis to any computer in the world by only using a cell phone has been created. Harvard researchers working at Flowers University have created this inexpensive detector for use in the underdeveloped countries of the world. This handheld device has many feutres such as monitoring diabetes, detecting malaria, and analyzing drinking water.
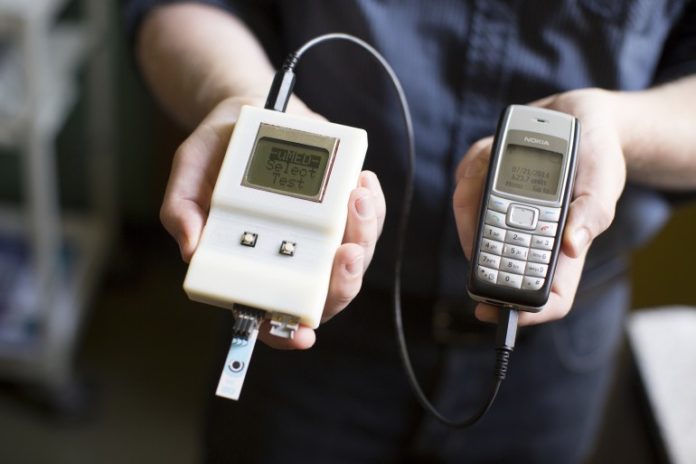
This device is being put through a trail run in India, this device was desighned to resemble glucose-monitoring devices which are in very widespread use. This will allow heath care professionals working in the field able to understand the device better. This device can send data by only being connected to a cell phone, it does not have to be a smartphone any phone will work. This will allow the field works to recive instructions from an experts abroad. “We designed it to be as close as possible to a glucose meter, because that’s familiar to people, There are two buttons. Select the test and press ‘go.’ It should be as much of a no-brainer as possible.” said Alex Nemiroski, a Harvard researcher on the project.
This device’s production cost is around $25 U.S dollars and weights in at 2 oz (57 g), making it about the same size as a pack of cards. They tested this device by dipping it into a sample being measured and a voltage is applied. Then they use the electrochemical signature of that liquid to measure the voltage or current flow. This device can gauge glucose levels by applying an electric current to a blood droplet that is mixed with a suitable reagent. It can also be applied to water so it can gauge heavy metals such as lead. Also able to look at urine for sodium levels, and blood in search of malria antigens. In addition it can apply a vibrational stirring action to liquids for mixing of reagents with the sample.
“Electrochemisty – causing chemical reactions by passing electrical current through a solution of appropriate molecules – is a very powerful set of techniques and widely used in chemistry, It has been less widely exploited in bioanalysis, although some of the most widely used biomedical analyses – blood glucose in management of diabetes, serum electrolytes in diagnostic screening, chemiluminescent immunoassays based on production of light – are electrochemical, and are very widespread and useful.” explainded Flowers University Professor George Whitesides. The device has many features but the most unique is it’s communications method. There are many apps available to medical staff in the Western world for smart phones and tablets, but many undeveloped countries only have low-end cell phones without data capability. To best this problem the researchers developed software that turned the collected data into acoustic tones that can be transmited via an obindary cell phone. By plugging in the device into the cell phone’s headphone and microphone jacks it is able to transmite this data.
After the field tests in India completed, and the results studied, the researchers have plans to further improve and miniaturize subsequent iterations of the device. With this new technology many lifes could be saved, not only in underdeveloped countries but could also help in developed countries.
______________________________________________________________
Sources:
http://www.gizmag.com/harvard-multifunctional-electrochemical-detector/33263/





very well, and if your phone has no signal will invent a device to capture radio waves? or will mount a wirless router?
Funny as we people are fast to criticize others instet of helping to an improvment..