Land mass and coastal habitats across the globe are at great risk of flooding if the sea levels continue to rise. This alarming issue has inspired Cartographer Jeffrey Linn to map the future of some of the most populated areas within the U.S, including Los Angeles, New York and Seattle. Now Linn has turned his attention to the Chinese coast, mapping the effects of future sea-level rise in some of the region’s most densely populated coastal areas.
The maps released depict the population megacenters surrounding Shanghai, Qingdong, and Haikou, regions; home to roughly 40 percent of the country’s population (approximately 542.8 million). “China has massive cities and populations right at sea level that are unmatched by anything that exists in North America,” Linn says. For comparison, the New York metropolitan area has a population of around 19 million, and Greater LA has around 18 million, the Pearl River Delta— located on the coast of the South China Sea, home of Hong Kong and East Asia’s largest megacity— is home to over 65 million people.
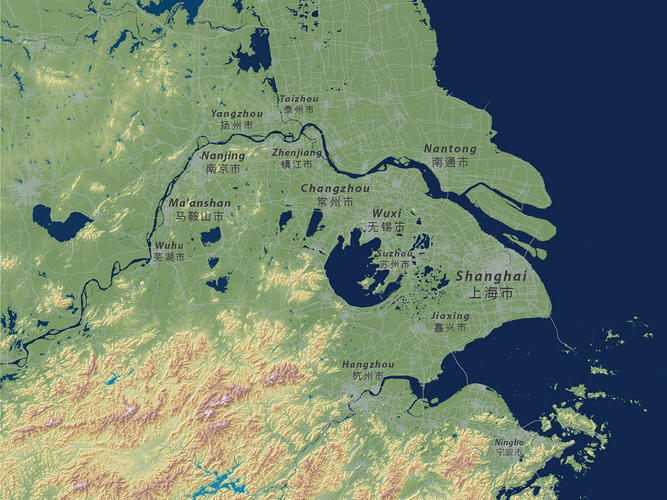
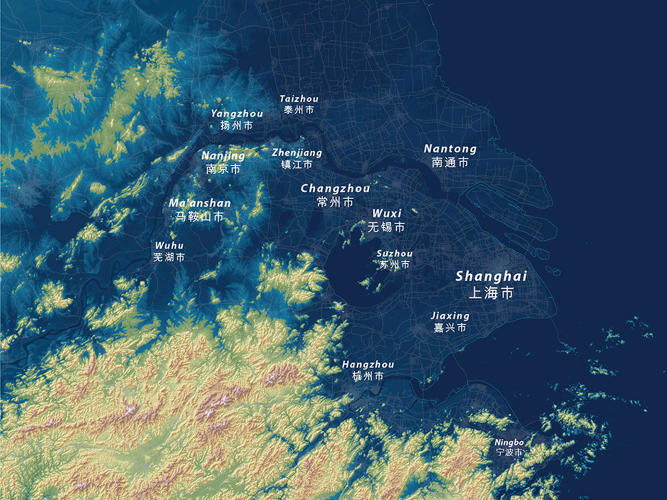
In the map below is the Yangtze River Delta— a region composed of three major areas: the Municipality of Shanghai, Zhejiang Province, and Jiangsu Province— home to a population of over 105 million. If both of the Earth’s ice sheets were to melt entirely, then an extensive amount of the region would become flooded.
“Greater Shanghai alone has over 24 million people, and will ultimately be devastated by rising seas … U.S. cities aren’t that large and we don’t have anywhere near the populations in low-lying estuary areas that will be at risk,” Linn told Fast Company.
With this significant sea-level rise, other regions would also accompany the Yangtze River Delta to the watery depths beneath the waves. The Fast Company Explains:
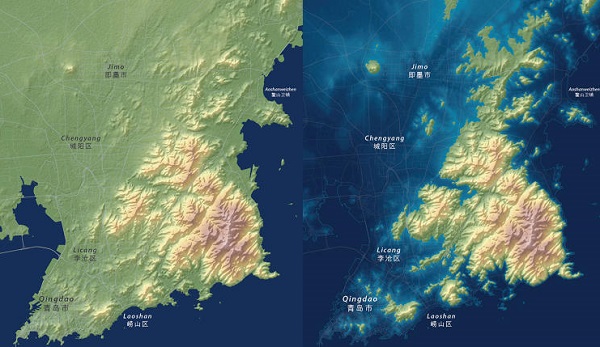
Up the eastern coast of China, the city of Qingdao is also at risk. In Linn’s maps, most of the region around Qingdao disappears, turning the peninsula into a series of small islands. By 2070, the city could have more than $600 billion in assets at risk from flooding.
Although Linn’s maps depict sea-level rises in the millennium ahead, the effects of melting ice sheets are already causing many short-term threats for these regions. Since the 1920’s, Shanghai has sunk roughly six feet, and its flood wall is weak; this means that the combination of a high tide and a typhoon could be devastating.
Also, if the body of ice completely melts, we won’t just lose land mass and densely populated cities: the entire ecosystem of the oceans will be drastically altered. The two ice sheets on Earth, which cover most of Greenland and Antarctica, contain more that 99 percent of the freshwater ice on Earth. As the fresh water ice sheets melts, the oceans’ salinity is reduced (sea water gets less salty), dramatically changing the oceans’ ecosystems, and ultimately threatening marine life and coral reefs.
It is therefore imperative that China and the rest of the world make good on their promise to fight climate change.
You want to support Anonymous Independent & Investigative News? Please, follow us on Twitter: Follow @AnonymousNewsHQ